16 Dec A Guide to Radiation: Background & Safety
 Radiation. It’s more than just a great way to get super powers.
Radiation. It’s more than just a great way to get super powers.
The extent of most people’s knowledge on radiation ends with colorful film and television storylines (ex. the radioactive spider bite that made Peter Parker Spider-Man or the gamma ray radiation that turned Bruce Banner into the Hulk).
However, radiation is so much more than a storytelling ploy. Radiation exists all around us and we are exposed to it every day.
And if you work in an industry where radiation levels could be potentially high, it is important that you understand just what radiation is and how to protect yourself against its harmful side effects.
What is Radiation?
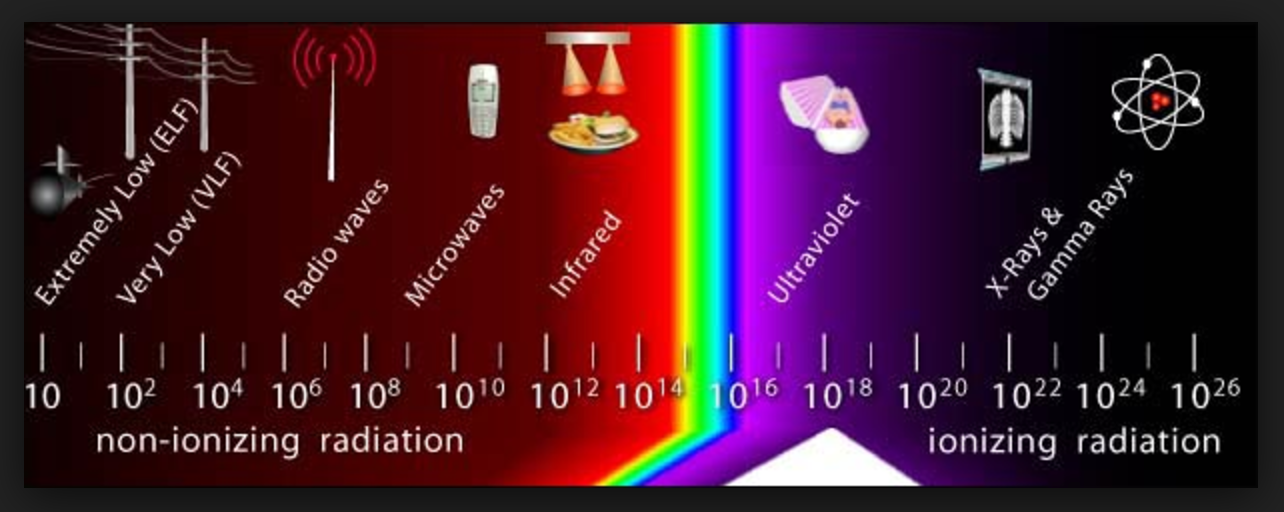
At its most basic definition, radiation is energy that travels through space as either high-speed particles or waves. There are two types of radiation: ionizing and non-ionizing, and together they make up the electromagnetic spectrum.
Ionizing Radiation
Ionizing radiation typically has more energy than non-ionizing radiation, thus allowing it to strip away an electron from a set and leave an unpaired electron behind (a process known as the ionizing of atoms and molecules). This process can be very damaging to cells and tissues, causing harm by means of:
- Breaking important chemical bonds
- Producing new, harmful chemical bonds that wouldn’t otherwise form
- Creating free radicals (reactive ions that interrupt normal body function and cause tissue and cellular damage)
- Damaging molecules and proteins responsible for cellular function
The amount of ionizing radiation you are exposed to will determine which (if any) of these harmful side effects will affect you. Additionally, extremely high doses of ionizing radiation may lead to radiation sickness, cancer, and death. Please note though, not all ionizing radiation is bad. Ionizing radiation is used in X-rays to look at bone, in other medical-related imaging processes, and the treatment of certain illnesses like cancer
Non-Ionizing Radiation
This type of radiation is essential to life and is all around us. Some examples of non-ionizing radiation you may be familiar with include:
- Ultraviolet Light
- Visible Light
- Microwaves
- Radio Waves
- Infrared Light
As mentioned, non-ionizing radiation doesn’t have as much energy as ionizing radiation. Accordingly, while non-ionizing radiation can make electrons wiggle, it is not powerful enough to strip away/remove electrons (ionizing atoms or molecules).
How Much Radiation is Safe?
Whether it comes from medical treatment, the air, the ground, etc., the fact is we are exposed to radiation every day. Though small amounts over short periods of time may have no effect, long-term exposure (like in the work place) could be hazardous to your health. As a general rule, when it comes to radiation the less exposure the better. However, the three main factors that contribute to your radiation level being safe or unsafe are: time, distance, and shielding.
Radiation & Your Health
While radiation is all around us, excessive exposure can cause damage to cells and tissue. Many industries have radiation in occupational settings. As such, it is vital for the employers of those companies to properly control their radiation levels and invest in employee safety training courses and corporate safety training courses for proper radiation safety and conduct.
To learn more about the radiation safety courses offered at Creation World Safety—your trusted corporate safety training and employee safety training company for Torrance, CA and the greater Los Angeles area—contact us today. We can’t wait to help you get started!


No Comments